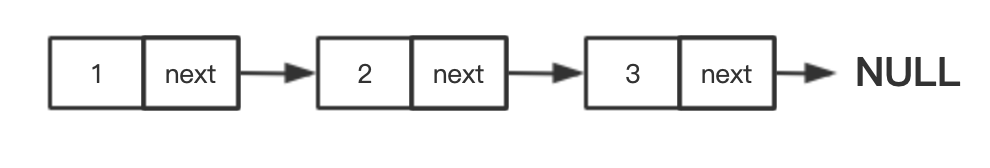
链表在Linux内核中可以说是一种最简单的、也是最普通的一种线性的数据结构。链表是一种存放和操作可变数量元素(通常我们称之为节点)的数据结构。
可以用最简单的数据结构来表示这样一个链表:
1 2 3 4 5 6 struct list_element { void *data; struct list_element *next ; };
下图描述一个链表结构体:
实现一种算法,找出单向链表的倒数第k个节点 示例:
1 2 3 输入: 1->2->3->4->5 和 k=2 输出:4
说明:
给定的k值是有效的。
解题思路
示例代码
C/C++示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 int kthToLast (struct listNode *head, int k) { struct listNode *p = struct listNode *q = int i = 0 ; while (k--) { p = p->next; } while (p) { p = p->next; q = q->next; } return q->val; } int kthToLast (struct ListNode* head, int k) { struct ListNode *p = struct ListNode *q = while (p) { p = p->next; k--; if (k<0 ) { q = q->next; } } return q->val; }
Go语言示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 func kthToLast (head *ListNode, k int ) int { fast := head slow := head for k>0 { fast = fast.Next k-- } for fast != nil { fast = fast.Next slow = slow.Next } return slow.Val }
给定一个链表,旋转该链表,将链表的每一个节点向右移动k个位置,其中k是非负数。 解题思路
遍历整个链表,找到链表的尾部同时获取链表的长度,将链表的尾部与链表头相连形成一个环。
然后通过取余计算计算k的余数。最后通过直接断开这个环,返回头指针即可。
Go语言 示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 func rotateRight (head *ListNode, k int ) if head == nil { return nil } n, p := 1 , head for p.Next != nil { p = p.Next n++ } p.Next = head k %= n for i :=1 ; i<= n-k; i++{ p = p.Next } head, p.Next = p.Next, nil return head }
实现一种算法,删除单向链表中间的某个节点(即不是第一个或者最后一个节点),界定你只能访问该节点。 解题思路
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 void deleteNode (struct listNode *node) { node->val = node->next->val; struct listNode *temp = node->next = node->next->next; free (temp); return ; }
1 2 3 4 func deleteNode (node *listNode) { node.Val, node.Next = node.Next.Val, node.Next.Next }
两数相加 给你两个非空链表来代表两个非负整数。数字最高位位于链表的开始位置,他们的每个节点只是存储一个数字。将这两数相加会返回一个新的链表节点,你可以假设除了数字之外,这连个数字都不会以零开头。
进阶:
如果输入链表不能修改该如何处理,换句话说,你不能对列表中的节点进行翻转。
解题思路
对两个参数链表进行翻转,翻转之后,对对应的位进行一个相加进位处理。
反转链表 给定一个单链表的头节点,请你反转链表,并且返回反转之后的链表。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 # 示例1: 输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5] 输出:[5,4,3,2,1] # 示例2: 输入:head = [1,2] 输出:[2,1] # 示例3: 输入:head = [] 输出:[]
解题思路:
(1)直接将链表prev和next指针原地反转
(2)返回新的链表头节点
示例代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 struct ListNode *reverseList (struct ListNode *head) { struct ListNode *prev =NULL ; struct ListNode *cur = struct ListNode *node =NULL ; while (cur) { node = cur->next; cur->next = prev; prev = cur; cur = node; } return prev; }
从尾到头打印链表 给定一个单向链表的头节点,从尾到头反过来返回每一个节点的值(用数据返回)。
1 2 3 4 # 示例1 输入:head = [1,3,2] 输出:[2,3,1] 限制:0 <= 链表长度 <= 10000
解题思路:
(1)先将链表进行反转,同时获取链表长度
(2)将反转后的链表的值从头到尾赋值给数组,并返回数组。
示例代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 struct ListNode *reverseList (struct ListNode *head, int *len) { *len = 0 ; struct ListNode *prev =NULL ; struct ListNode *cur = while (cur) { (*len)++; struct ListNode *node = cur->next = prev; prev = cur; cur = node; } return prev; } int * reversePrint (struct ListNode* head, int * returnSize) { if (!head) { *returnSize = 0 ; return NULL ; } if (!returnSize) { return NULL ; } int len = 0 ; int i = 0 ; struct ListNode *new_list = int *retArray = (int *)malloc (sizeof (int ) * len); if (!retArray) { return NULL ; } struct ListNode *ptr = while (ptr) { retArray[i++] = ptr->val; ptr = ptr->next; } *returnSize = len; return retArray; }
删除排序链表中的重复元素 给定一个已排序的链表的表头head,删除所有重复的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次,返回已排序的链表。
1 2 3 4 5 输入:[1,1,2] 输出:[1,2] 输入:head = [1,1,2,3,3] 输出:[1,2,3]
解题思路:
(1)将当前节点与下一个节点进行比较
(2)如果两个节点的值相同,则将下一个节点释放表,以此类推。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 struct ListNode* deleteDuplicates (struct ListNode* head) { if (!head) { return NULL ; } struct ListNode *node = struct ListNode *tmp =NULL ; while (node) { if (node->next && (node->next->val == node->val)) { tmp = node->next; node->next = node->next->next; free (tmp); } else { node = node->next; } } return head; }
相交链表
解题思路:
(1)
(2)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode (struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) { if (!headA || !headB) return NULL ; struct ListNode *node1 = struct ListNode *node2 = while (node1 != node2) { node1 = node1 ? node1->next : headB; node2 = node2 ? node2->next : headA; } return node1; }
移除链表元素 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 输入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6 输出:[1,2,3,4,5] 输入:head = [], val = 1 输出:[] 输入:head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7 输出:[]
解题思路:
(1)在前面增加一个哨兵节点
(2)使用迭代的方式,进行链表遍历操作
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 struct ListNode* removeElements (struct ListNode* head, int val) { if (!head) return NULL ; struct ListNode *guard_head =struct ListNode*)malloc (sizeof (struct ListNode)); if (!guard_head) return NULL ; guard_head->next = head; struct ListNode *node = struct ListNode *tmp =NULL ; while (node->next != NULL ) { if (node->next->val == val) { tmp = node->next; node->next = node->next->next; } else { node = node->next; } } return guard_head->next; }